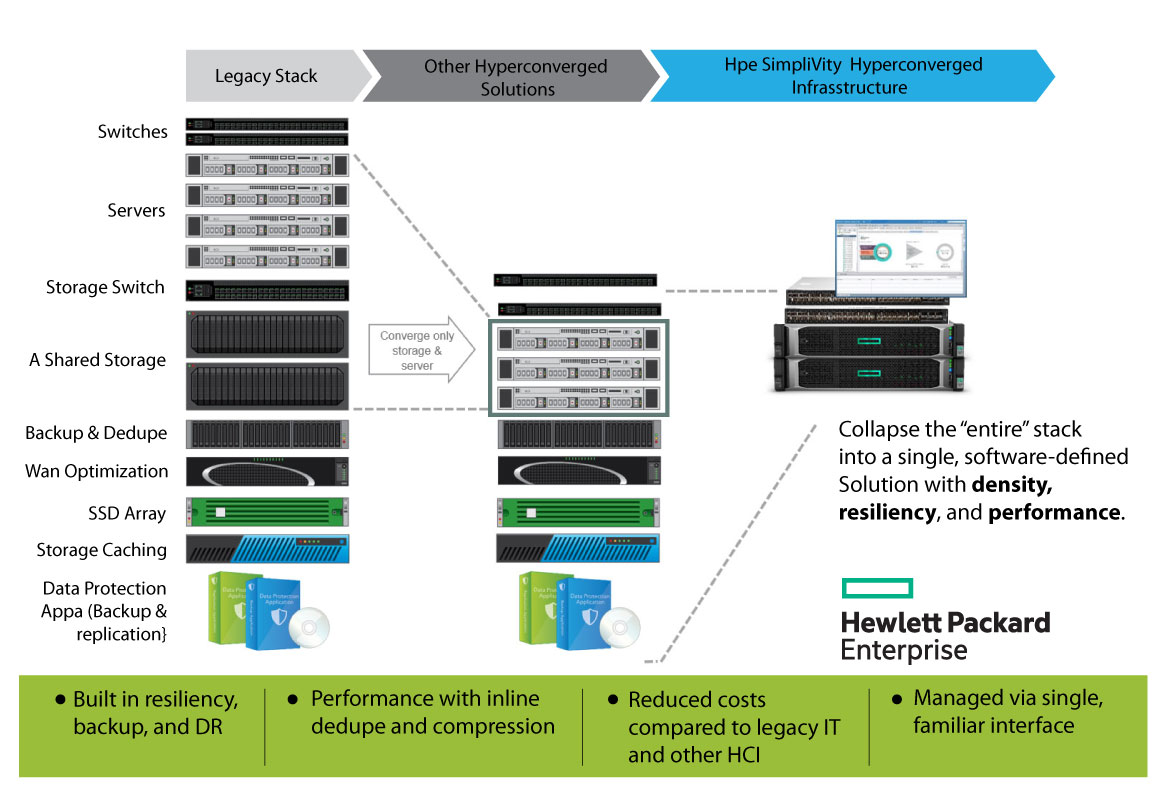
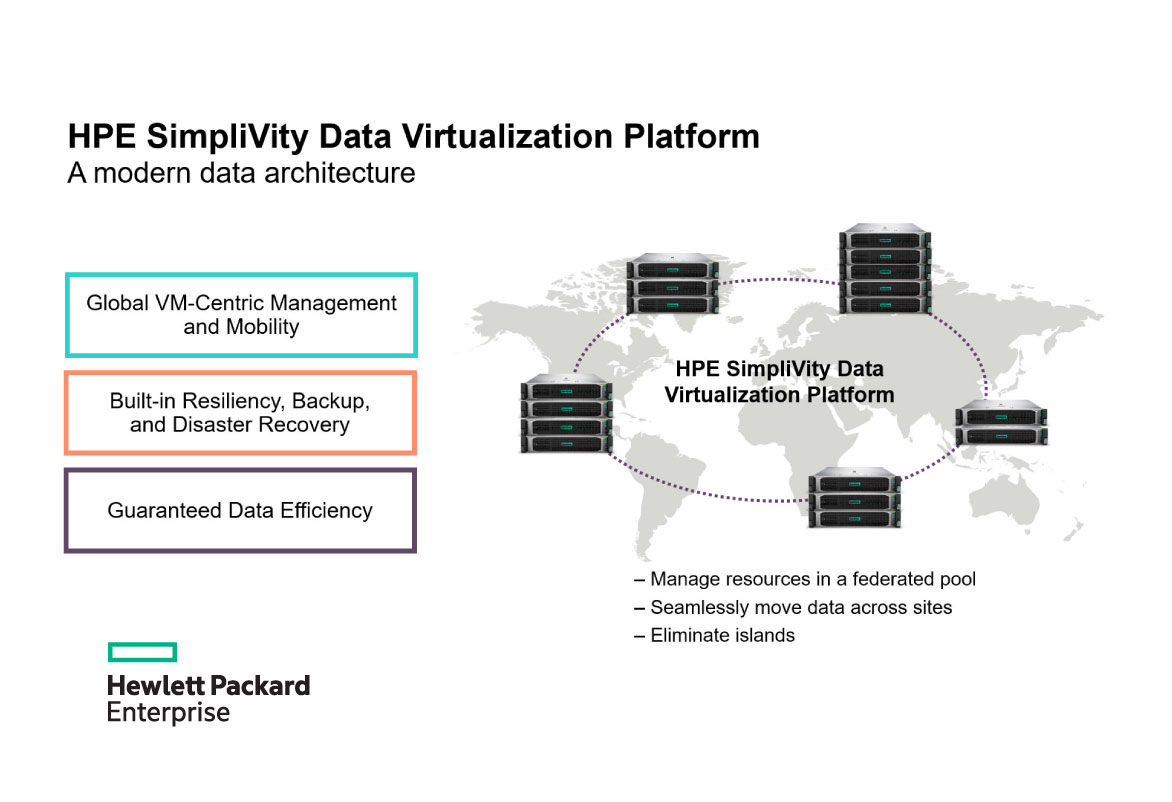
Introduction:
In earlier times, many companies deployed hardware servers to provide services to network users and customers. In an effort to be efficient, each service or workload such as email, web, print, directory and file was delivered from a separate server. This had the advantage that work could be carried out on an individual server without directly affecting the other machines. Additionally, failure of a single server did not interrupt services supplied by the remaining functioning systems.
Some downsides to this arrangement include the potential of multiple points of hardware failure, multiple complex hardware systems to manage, introduction of a new service could potentially require costly hardware acquisition and high energy costs. Moreover, very rarely was the full power of the hardware harnessed by the running applications. On top of all that, server redundancy added complexity and costs.